Agricultural equipment repository
1. Product Detail information
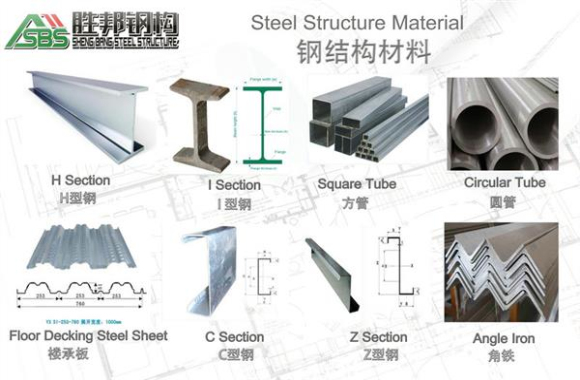
1)Steel Structure material
1.Welded Stud Shear Connectors: Shear connector studs shall conform to the requirements of Section 7.3, Type B of the latest edition of the ANSI/AASHTO/AWS D1.5 Bridge Welding Code and the following.
2.Finished studs shall be of uniform quality and condition, free from injurious laps, fins, seams, cracks, twists, bends or other injurious defects. Finish shall be as produced by cold drawing, cold rolling or machining.
3.The manufacturer shall certify that the studs as delivered are in accordance with the material requirements of this section. Certified copies of in-plant quality control test reports shall be furnished upon request. The Engineer may select, at the Contractor's expense, studs of each type and size used under the contract, as necessary for checking the requirements of this section.
4. Unfilled Tubular Steel Piles: Unfilled Tubular Steel Piles shall conform to ASTM A252, Grade
5, with chemical requirements meeting ASTM A53, Grade B.
Good shelter is essential to an agri-related business. This is why horses, livestock, hay, grain, crops and farm equipment all need protection from the elements.
Steel agricultural buildings are an ideal substitute for traditional wooden structures, thanks to their unparalleled strength and durability. They are maintenance free and are available in many sizes and models to suit your needs.Each arch building includes an assembly manual that is easy to follow, ensuring ease of construction. Steel agricultural buildings are an ideal substitute for traditional wooden structures, thanks to their unparalleled strength and durability. They are maintenance free and are available in many sizes and models to suit your needs.
2. product details
|
Product Name
|
Prefabricated Steel Structure Building
|
|
Specification
|
Foundation
|
Concrete and Steel
|
|
Support
|
X or V types, angle steel or round tube
|
|
Surface
|
Two layers and anti-rust paint
|
|
Color
|
White, Grey, Blue, Green, etc
|
|
size
|
Designed by your requirement
|
|
Main component
|
Base materials
|
Cement and steel foundation bolts
|
|
Main frame
|
H beam (welded or hot rolled)
|
|
Material
|
Q35B,Q345B
|
|
Purlin
|
C purlin (C120-320) or Z Purlin (Z100-200)
|
|
Bracing
|
Tie bar, lateral bracing, column bracing, knee bracing, etc
|
|
Bolt
|
Normal bolt, high strength bolts, Galvanized bolt
|
|
Roof & wall
|
Sandwich panel, steel corrugated sheet
|
|
Door
|
Sliding door , rolling shutter
|
|
Window
|
PVC window, aluminum-alloy Window
|
|
Accessories
|
Skylight, ventilation, downpipe and galvanized gutter etc .
|
3. Introduction of steel hangar
1)The strength of steel hanger comes from the use of beams,the key components are manufactured from steel or galvanized steel.
2) the modular steel garage need different spans according their parts.
3) the sandwich panels can be used in wall panels or roof,and the price is associated with thier features,different characture has different price.
4) sandwich panel insulation layer may be made of different materials, such as glass wool, polyurethane, rock wool, which have varying levels of insulation.
5) the steel structure building components steel columns, steel beams, steel and rigid support, etc.,so,steel structure is suit for big buildings.
4. steel structure design common specifications are as follows:
1) "technical specification for cold formed steel structures" (GB50018-2002)
2) "just construction quality acceptance" (GB50205-2001)
3) "for the welding of steel structure technical specification" (JGJ81-2002-2002 J218)
4) "technical specification for steel structure of high rise civil building" (JGJ99-98)

5. Steel structure earthquake-resistance date
Structural steel used in the seismic force resisting system (SFRS) shall satisfy the requirements of Specification Section A3.1, except as modified in these Provisions. The specified minimum yield stress of steel to be used for members in which inelastic behavior is expected shall not exceed 50 ksi (345 MPa) for systems defined in Chapters E, F, G and H, except that for systems defined in Sections E1, F1, G1, H1 and H4 this limit shall not exceed 55 ksi (380 MPa). Either of these specified minimum yield stress limits are permitted to be exceeded when the suitability of the material is determined by testing or other rational criteria.
User Note: This section only covers material properties for structural steel used in the SFRS and included in the definition of structural steel given in Section 2.1 of the AISC Code of Standard Practice. Other steel, such as cables for permanent bracing, is not covered. Steel reinforcement used in components in composite SFRS is covered in Section A3.5.
6.STRUCTURAL DESIGN DRAWINGS AND SPECIFICATIONS
Structural design drawings and specifications shall indicate the work to be performed, and include items required by the Specification, the AISC Code of Standard Practice for Steel Buildings and Bridges, the applicable building code, and the following, as applicable:
1) Designation of the SFRS
2) Identification of the members and connections that are part of the SFRS
3) Locations and dimensions of protected zones
4) Connection details between concrete floor diaphragms and the structural steel elements of the SFRS
5) Shop drawing and erection drawing requirements not addressed in Section I1


